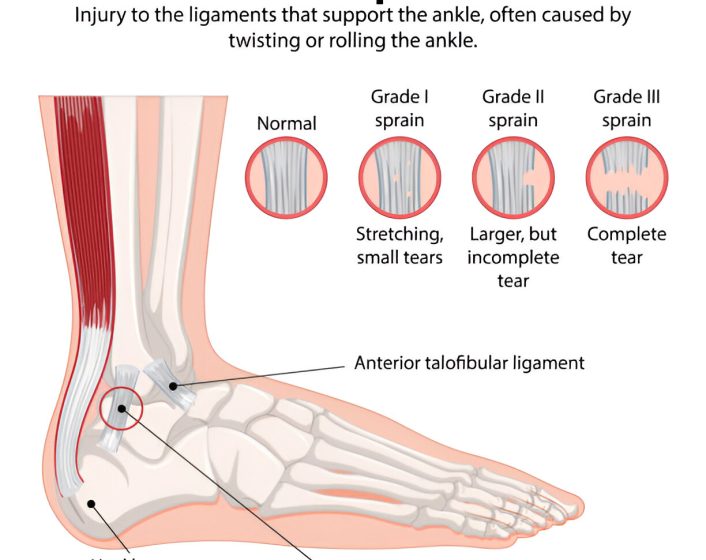
The Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATFL) is one of the key ligaments in the ankle that stabilizes the joint by connecting the fibula to the talus bone. An ATFL injury, commonly known as a sprain, occurs when this ligament is stretched or torn, usually due to twisting or rolling of the ankle. This injury is prevalent in sports and activities involving sudden changes in direction. Symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected ankle.
Treatment for an Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATFL) injury, commonly an ankle sprain, depends on the severity of the injury. Initial treatment usually involves the RICE method—Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation—to reduce pain and swelling. Over-the-counter pain relievers may also be recommended. As healing progresses, physical therapy plays a crucial role in restoring strength, flexibility, and stability to the ankle. Therapy typically includes exercises to improve balance and prevent future sprains. In more severe cases, where the ligament is significantly torn, bracing or surgical repair may be necessary to ensure proper healing and prevent chronic instability or repeated injuries.
When it comes to treating ATFL injuries, choosing the right care provider is essential for a full and lasting recovery. Here’s why we are the best choice for your ankle treatment: